IEEE 802.15.4
Information Taken from IEEE 802.15.4-2011. Additional information can be found in the "Official" Wikipedia article linked below or the IEEE website (also linked below).
IEEE Official Standards for 802.15
Basics
- ~10m Range Devices
- Frequency Ranges
- 868-868.6 MHz
- 902-928 MHz
- 2400-2483.5 MHz
Data Transfer
Beacon Enabled
Figures to be added soon.
Beacon Disabled
Figures to be added soon.
Device Types
- Full-Function Device
- Personal Area Network Coordinator (PAN Coordinator)
- Device
- Reduced-Function Device
- Device
Frame Structures
- Beacon Frame
- Data Frame
- Acknowledgement Frame
- MAC Command Frame
Busy Channel Avoidance
CSMA-CA
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance.
Figure to be added soon.
ALOHA
Devices transmit without sensing the medium or waiting a specific amount of time. This protocol is best for a lightly loaded network.
MAC Layer
The MAC Layer is responsible for the following:
- Generating network beacons if the device is a coordinator
- Synchronizing to network beacons
- Supporting PAN association and disassociation
- Supporting device security
- Employing the CSMA-CA mechanism for channel access
- Handling and maintaining the GTS mechanism
- Providing a reliable link between two peer MAC entities
PHY Layer
The PHY Layer is responsible for the following:
- Activation and deactivation of the radio transceiver
- Energy detection (ED) within the current channel
- Link quality indicator (LQI) for received packets
- Clear channel assessment (CCA) for carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance(CSMA-CA)
- Channel frequency selection
- Data transmission and reception
- Precision ranging for ultra-wide band (UWB) PHYs
- Minimum Transmit Power = -3dBm
Modulation Schemes
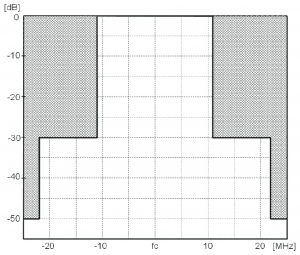
- O-QPSK - Offset Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying, Direct Sequency Spread Spectrum (DSSS) employing O-QPSK
- 868 MHz Band
- 915 MHz Band
- 2450 MHz Band
For 2450 MHz Band, the Power Spectral Density Mask is:
| Frequency (from Carrier) | Relative Limit | Absolute Limit |
|---|---|---|
| <math>\pm</math>3.5 MHz | -20 dB | -30 dBm |
- BPSK - Binary Phase Shift Keying, DSSS employing BPSK
- 868 MHz Band
- 915 MHz Band
- ASK - Amplitude Shift Keying, Parallel Sequence Spread Spectrum (PSSS) employing ASK and BPSK modulation
- 868 MHz Band
- 915 MHz Band
- CSS - Chirp Spread Spectrum, CSS employing differential quadrature phase-shift keying (DQPSK) modulation
- 2450 MHz Band
- UWB - Ultra Wide Band, Combined Burst Position Modulation (BPM) and BPSK modulation
- 3-10 GHz Bands
Data Rates
| PHY (MHz) | Frequency Range (MHz) | Chip Rate (kchips/s) | Modulation | Bit Rate (kb/s) | Symbol Rate (ksymbol/s) | Symbols |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 868 | 868-868.6 | 300 | BPSK | 20 | 20 | Binary |
| 915 | 902-928 | 600 | BPSK | 40 | 40 | Binary |
| 2450 DSSS | 2400-2483.5 | 2000 | O-QPSK | 250 | 62.5 | 16-ary Orthogonal |
Channel Numbering
868, 915, 2450 MHz Bands
<math> F_c = 868.3 \, </math>
<math> F_c = 906 + 2(k-1) \, </math> for k = 1,2,...,10
<math>
F_c = 2405 + 5(k-11) \,
</math>
for k = 11,12,...,26
k is the channel number
CSS PHY
| Channel Number | Frequency (MHz) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 2412 |
| 1 | 2417 |
| 2 | 2422 |
| 3 | 2427 |
| 4 | 2432 |
| 5 | 2437 |
| 6 | 2442 |
| 7 | 2447 |
| 8 | 2452 |
| 9 | 2457 |
| 10 | 2462 |
| 11 | 2467 |
| 12 | 2472 |
| 13 | 2484 |
Security
- Most security architectural elements can be implemented at higher layers
- Security relies on Symmetric-Key Cryptography
- Uses either Link Keys (for two devices) or Group Keys (for multiple devices)
- Is responsible for data confidentiality, authenticity, and replay protection